Create a JPA Project
There are a number of steps to create a JPA project. Follow along with this walkthorugh and pretty soon you'll have a good idea how to create a JPA project. Due to differences in Eclipse versions, your screens may differ slightly. You can create a JPA project for a Java project or for a Dynamic Web Project.
1) First Create a New Java Project….
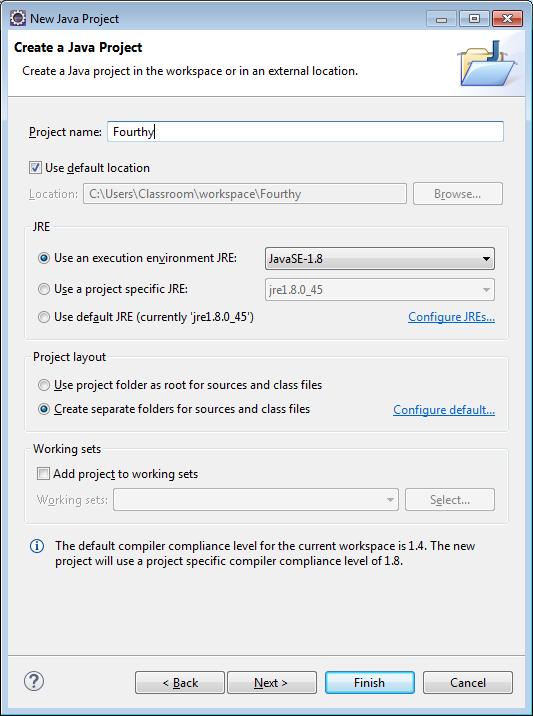
2) Click the Next button (not the Finish button) and get to the Java Settings screen.
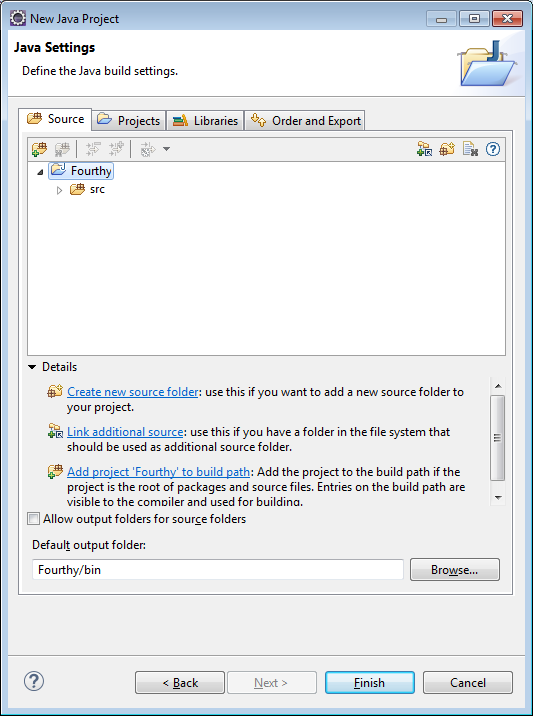
3) Click on the Libraries tab so you can add the necessary jar files to the build path. You will need to add 3 jar files: EclipseLink, JavaPersistence and OJDBC.
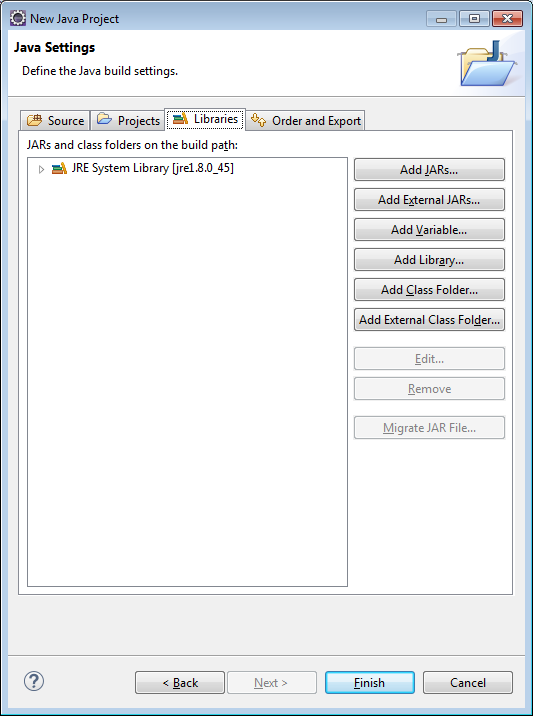
4) Click on the Add External JARs… button and select the eclipselink.jar file and click Open.
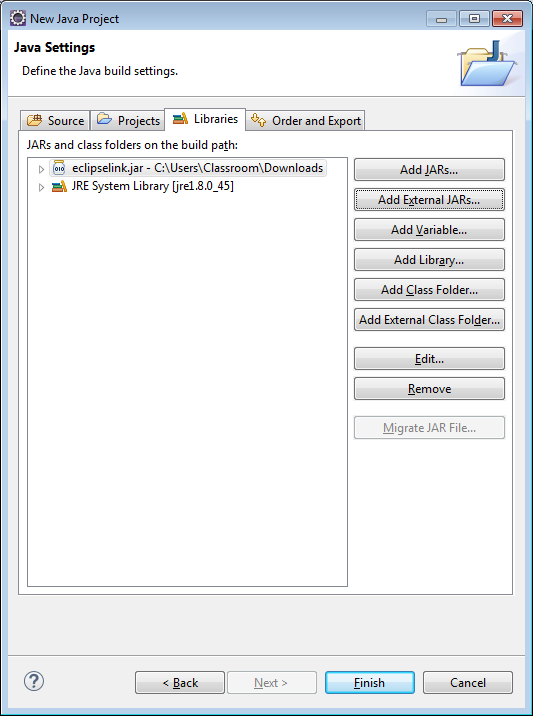
5) Click on the Add External JARs… button and select javax.persistence_2.1.0.v201304241213.jar (or whatever the current version is)
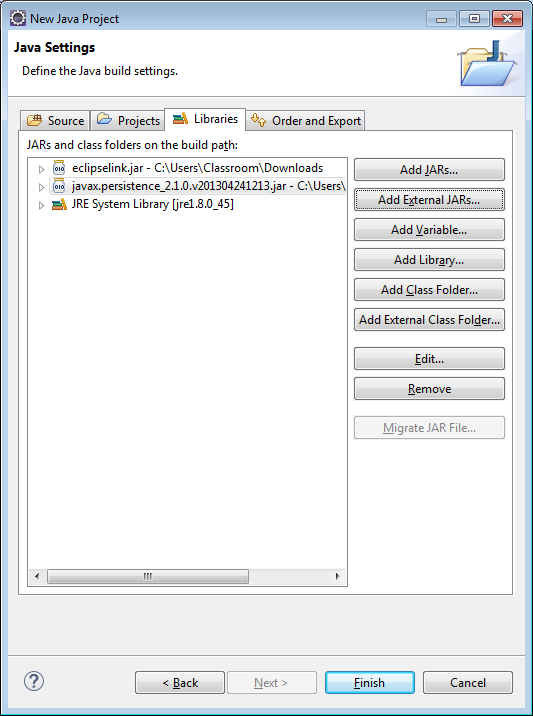
6) Click on the Add External JARs… button and select ojdbc6.jar (or whatever the current version is) and click Finish.
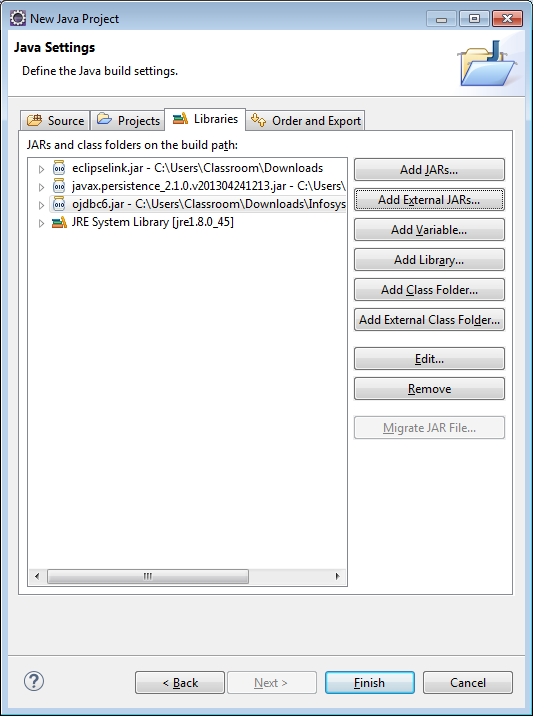
7) Right-Click your project in the Project Explorer and select Properties from the drop-down.
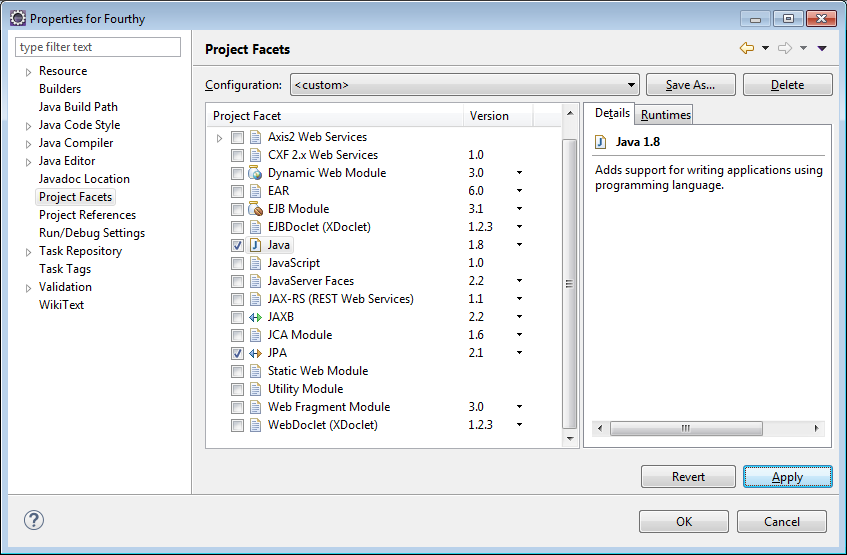
8) Select Project Facets from the list on the Left…
9) If you see the screen below, you need to click the “Convert to faceted form…” link…
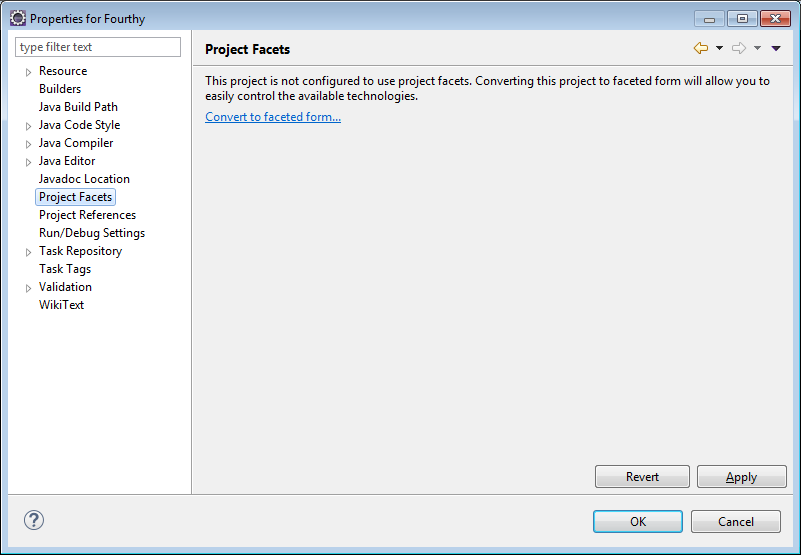
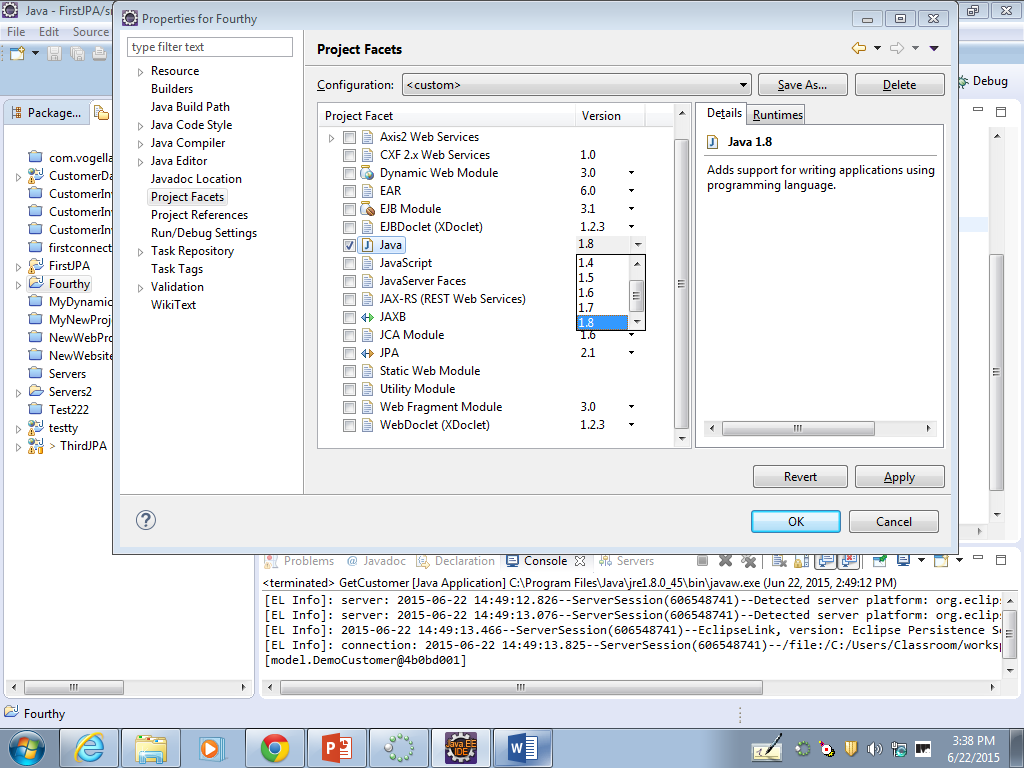
10) This project has a Java version level that is too low. The Java version should be 1.7 or higher.
Make the window a little wider so that you can see the controls to increase the Java level.
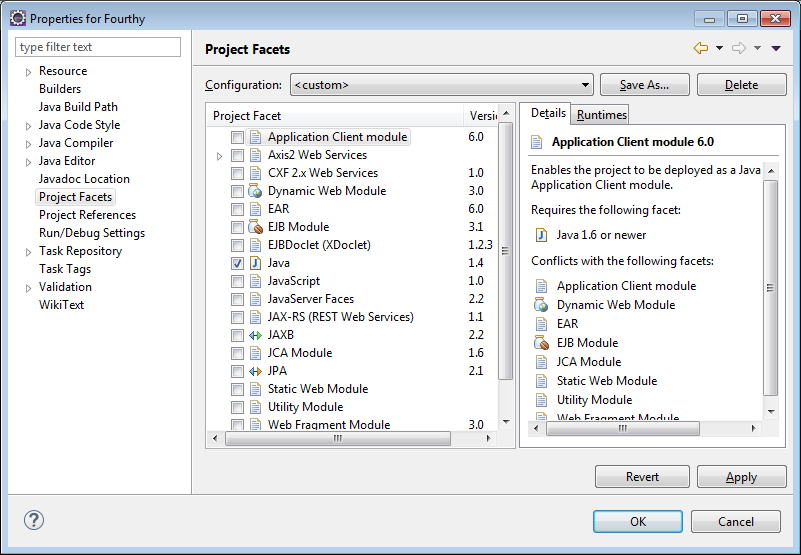
11) Click the drop-down triangle next to the number that is on the line with the Java Project Facet.
12) Click on the checkbox next to JPA and you will be asked to do some configuration. Click the link and get the following screen. Set the following:
Platform: to EclipseLink
JPA Implementation Type: Disable Library Configuration
Connection: to the name of your connection.
Once this is done click the connect link immediately under and to the right of the connection drop down.
And then click OK.
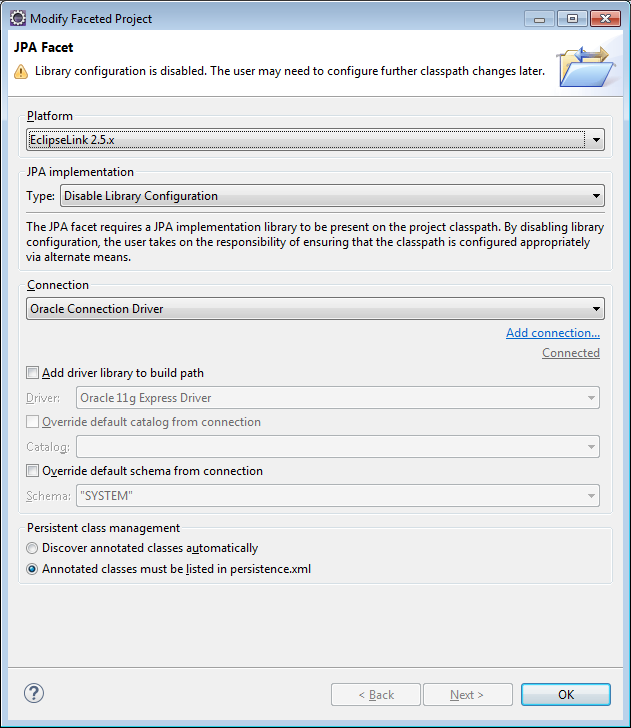
13) Click Apply to save your JPA settings…
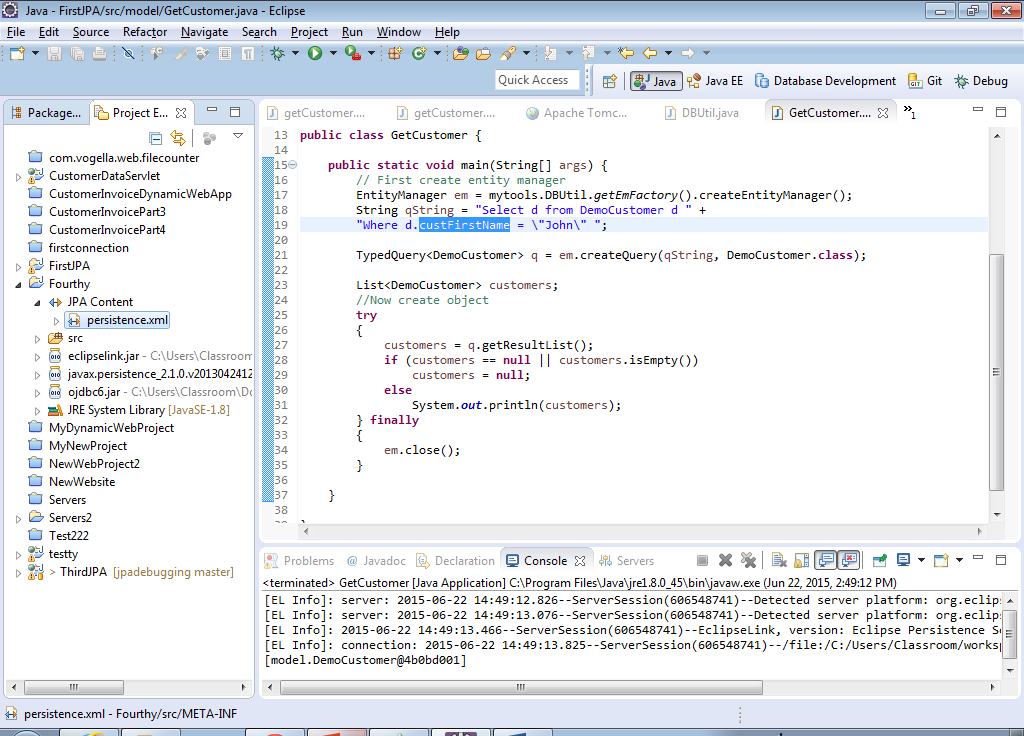
14) Look in the JPA Content container inside your project and double-click the persistence.xml file.
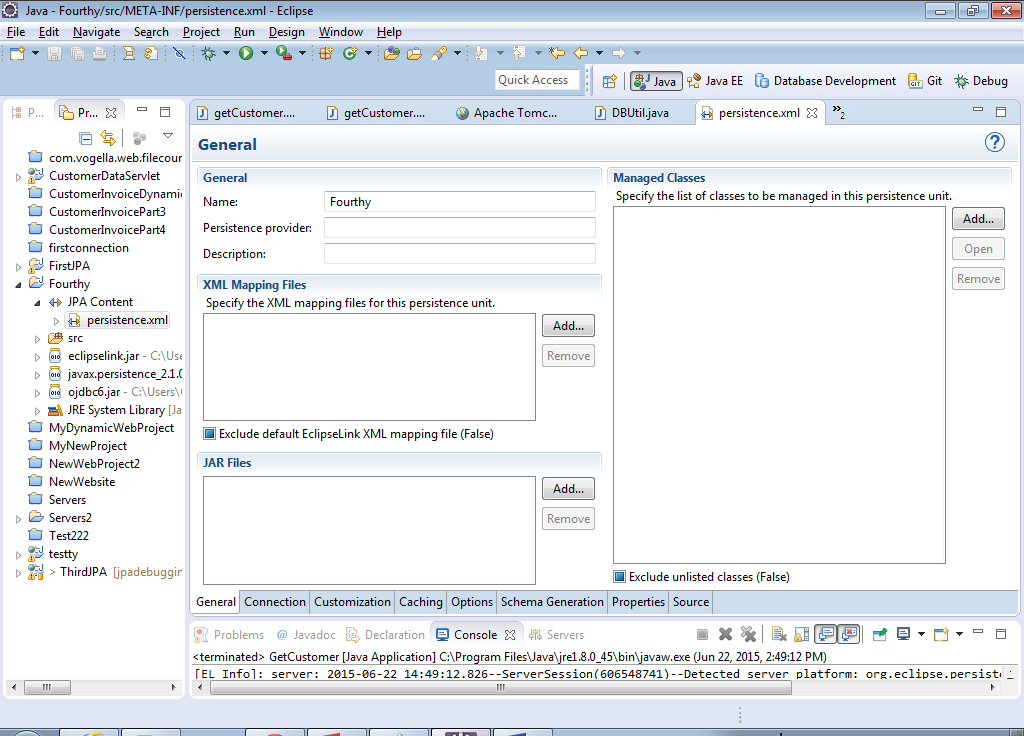
15) This is the dialog box for configuring your persistence.xml file
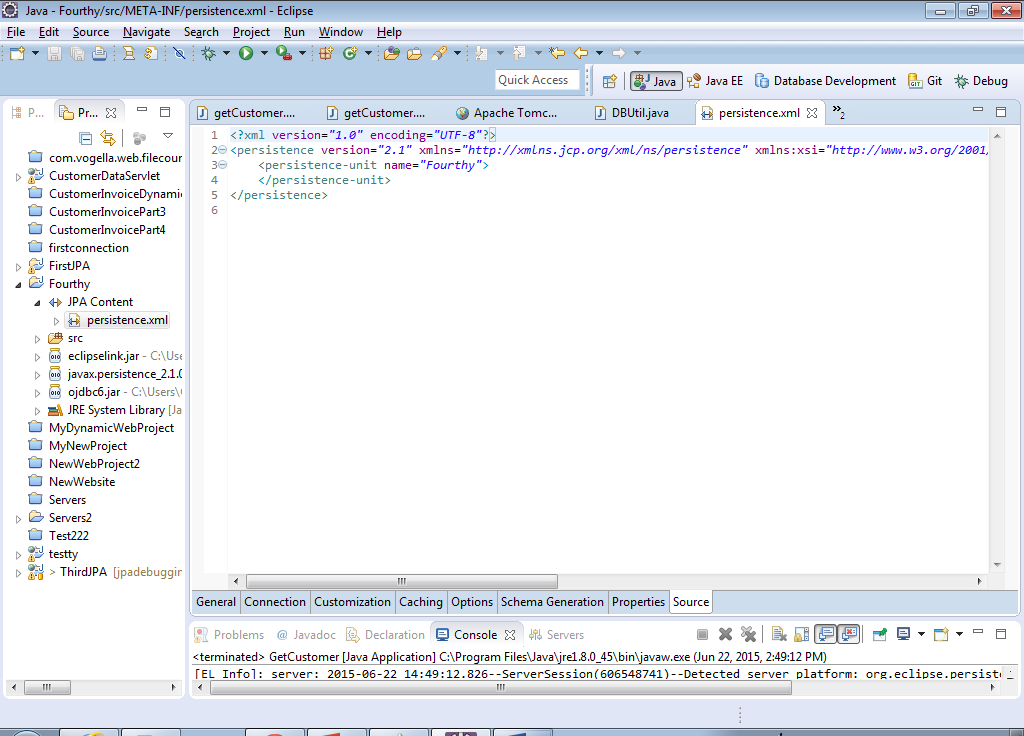
16) If you click the General tab, you will see the raw xml of the persistence file. It doesn’t look like much yet but as we set our configuration more tags will be added.
17) On the General tab, set the Persistence Provider to org.eclipse.persistence.jpa.PersistenceProvider
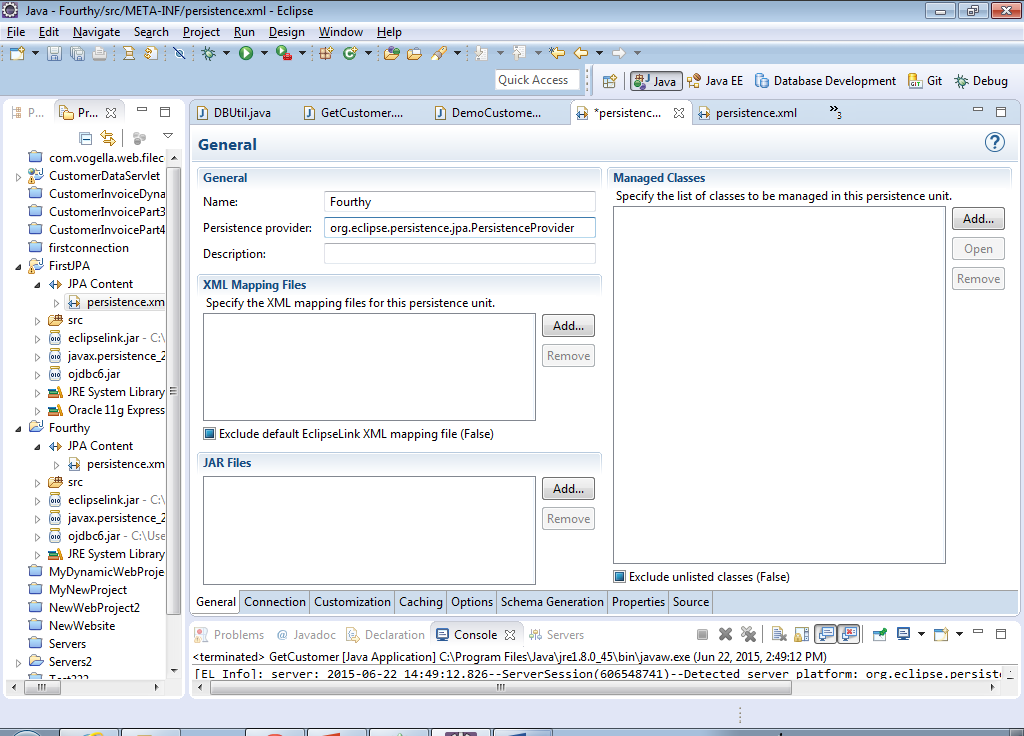
18) Uncheck the Exclude unlisted classes checkbox…
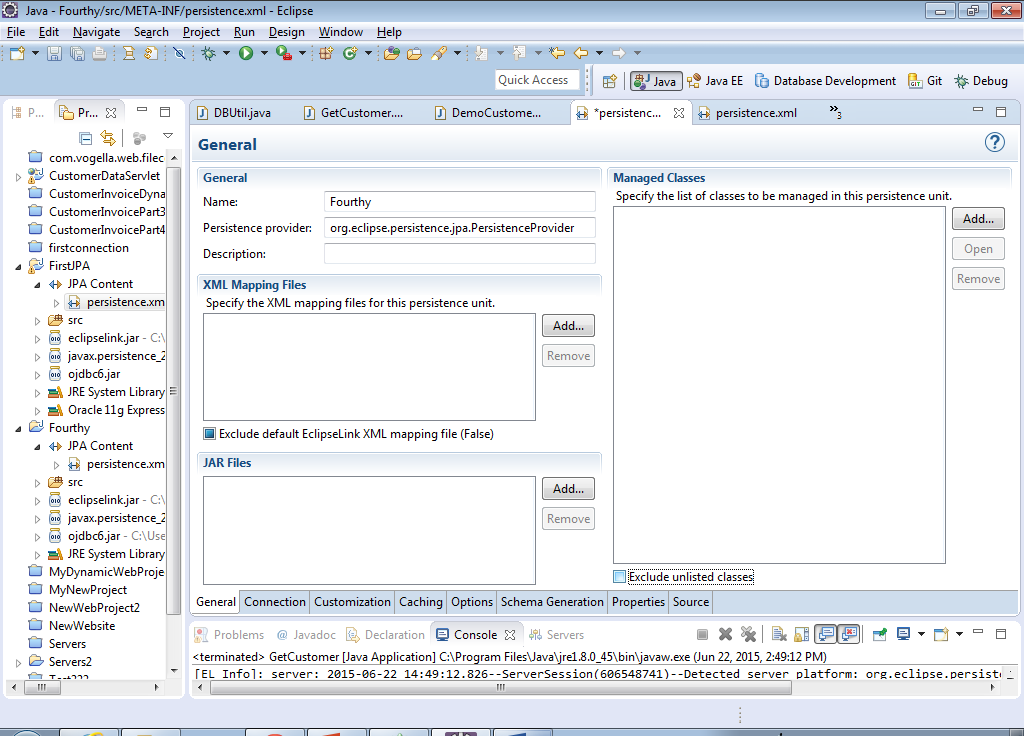
19) On the connection tab, change the Transacation Type to Resource Local…
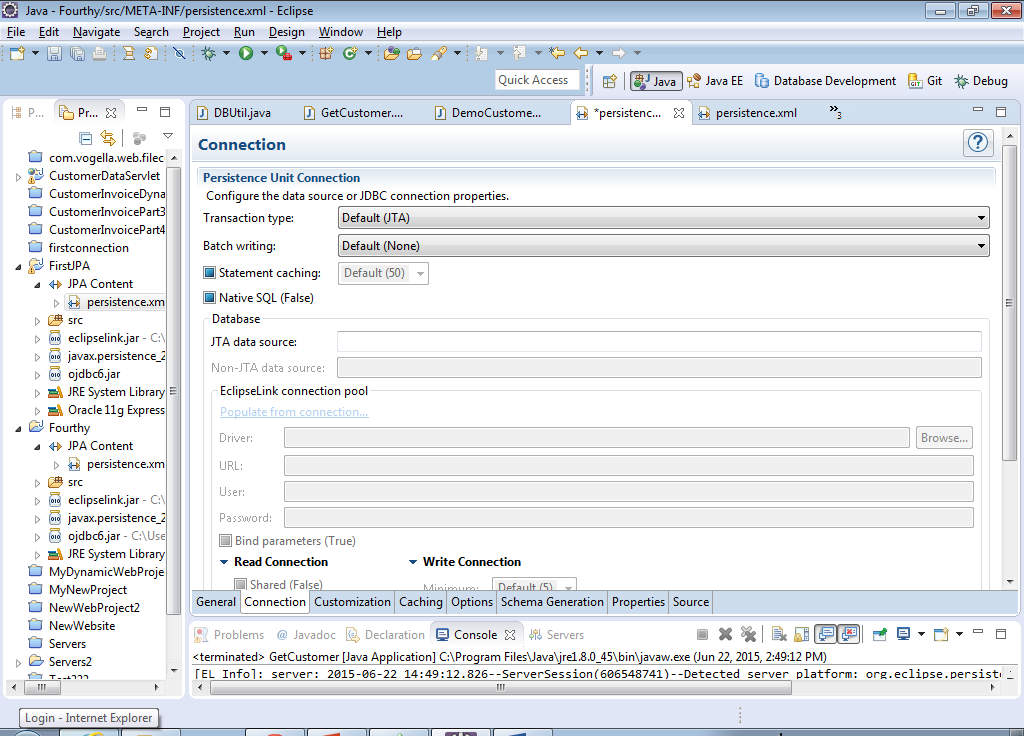
20) After that, click the Populate from connection link…
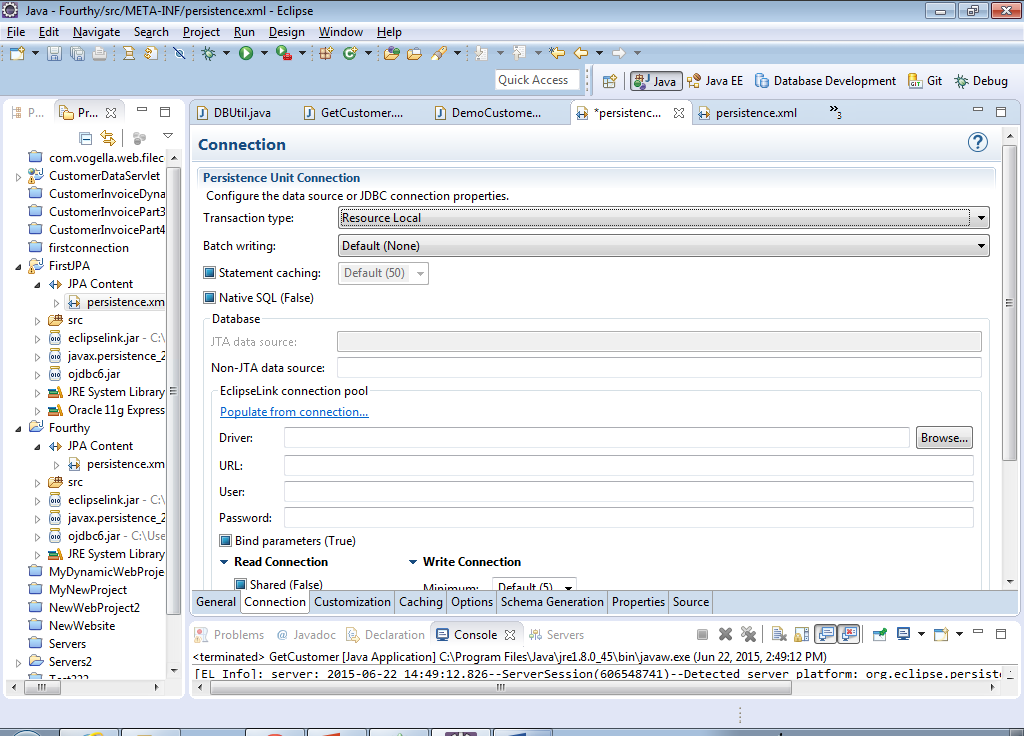
21) A dialog will appear asking you to select your connection, click Ok after you have done so…
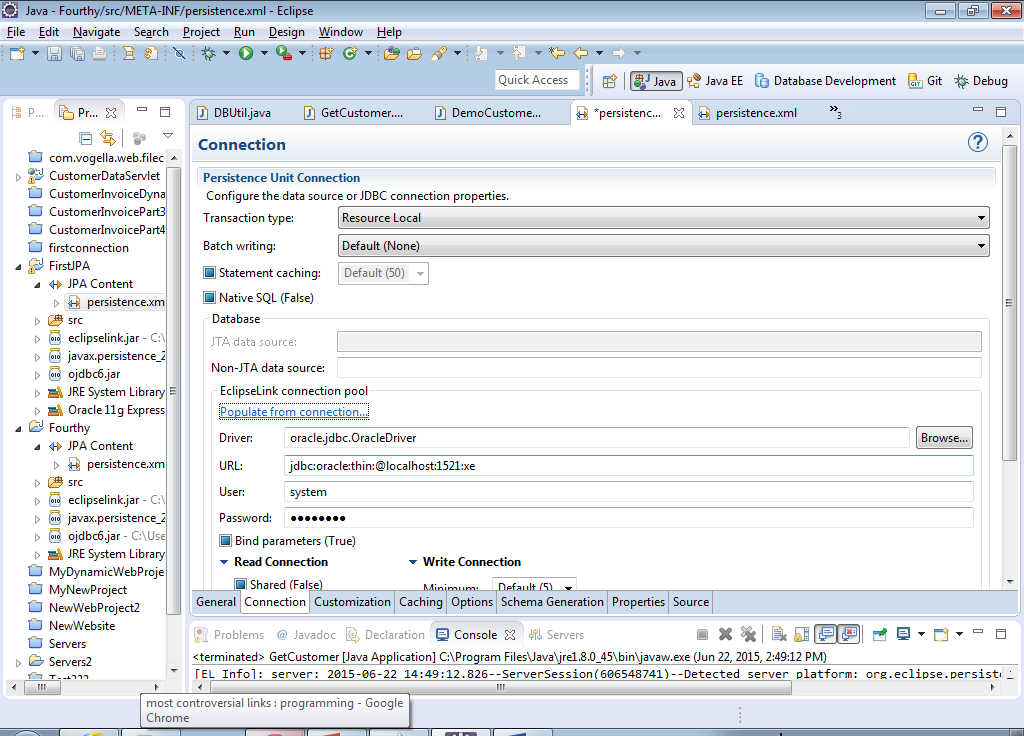
22) The dialog should now look like this… Note: the URL may be slightly different depending on your system. It’s also possible you have a different value for User.
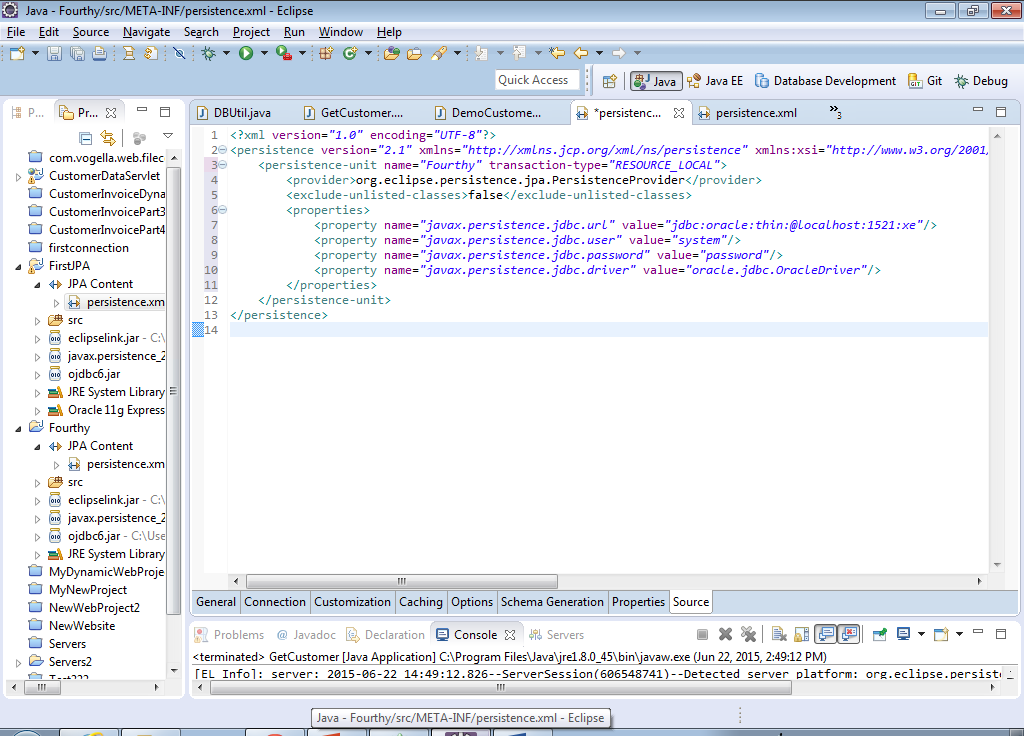
23) If you click on the source tab, the XML should now look approximately like this…
Save the file changes (click the icon in Eclipse to save) and you are done…
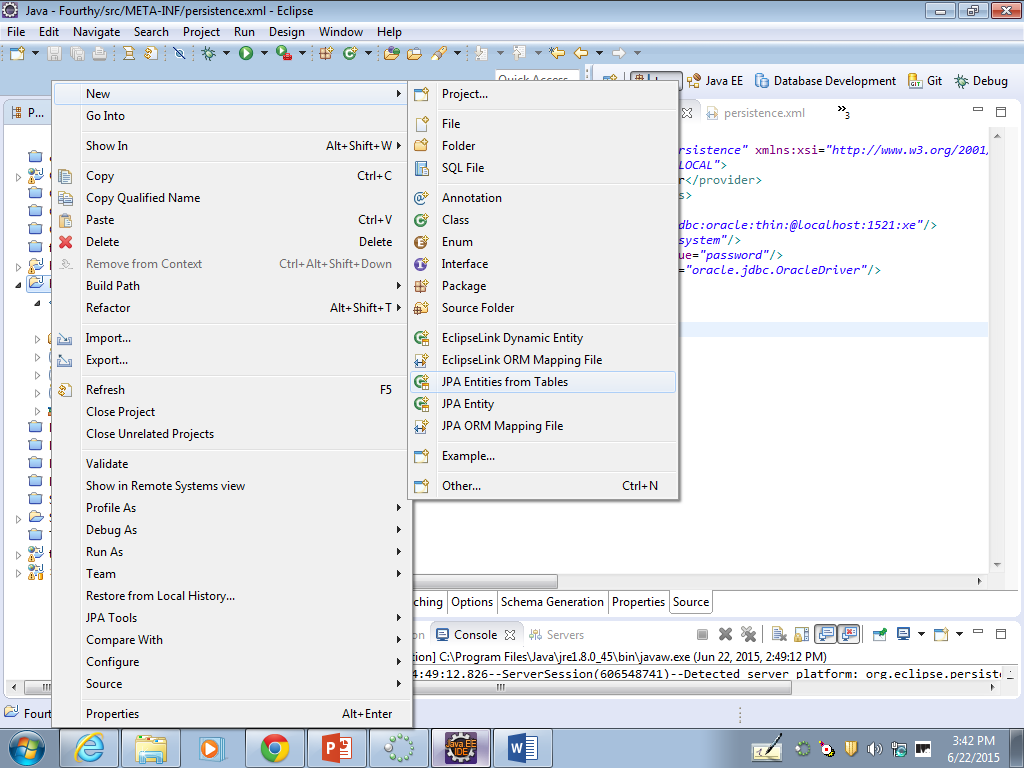
24) Right-Click your project and Select New… JPA Entities from Tables…
25) This is the Generate Custom Entities dialog. If you completed all the previous steps you should see your connection listed. When connected you will see your schemas and tables listed…
26) Once you have selected the Connection, the Schema and at least one Table, you should see the Next button activate.
27) This screen will be blank if you have only selected one table (and possibly even if you have selected multiple tables but they don’t have any relationship to each other)
28) Hit Next on this screen too…
29) Hit Next again (but this is where you would customize the name of the class and/or the names of the columns)…
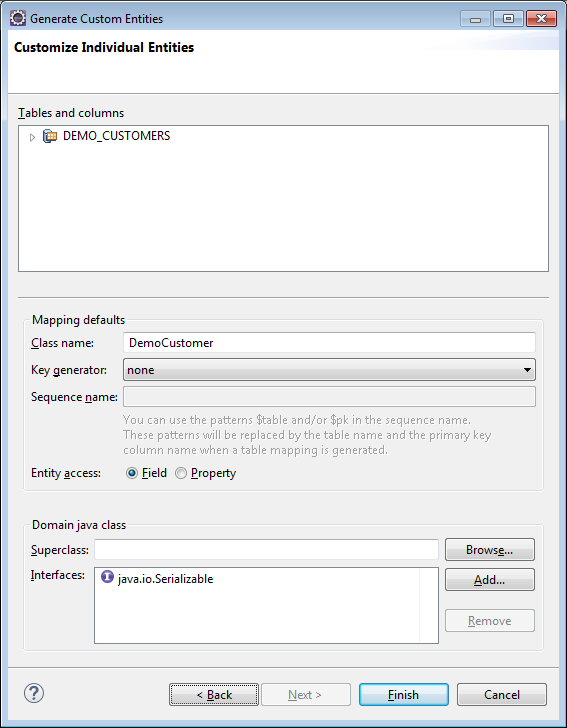
30) Once you click Finish, you should right-click the project name again…
31) Select New… Class…
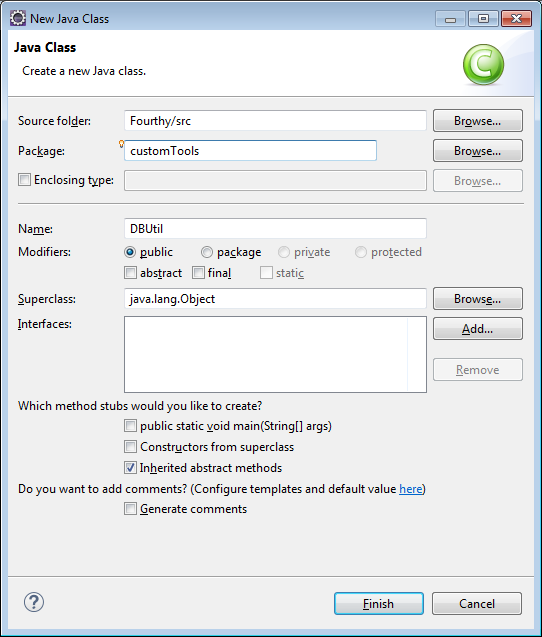
32) This is the class creation dialog, the main things you want to do are set your Package to customTools, your name to DBUtil and then click Finish…
33) Eclipse will open your DBUtil.java class ready for editing. Edit it to look something like this…
Replace name of your persistence unit with the name of your persistence unit.
package customTools;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.persistence.Persistence;
public class DBUtil {
private static final EntityManagerFactory emf =
Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("name of your persistence unit");
public static EntityManagerFactory getEmFactory() {
return emf;
}
}
34) Right-Click the Project Name and Select New… Class…
35) For this class just pick a name and check the public static void main(String[] args) checkbox…
36) After you click Finish, edit the class to look like this:
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import data.DBUtil;
public class QS3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManager em = DBUtil.getEmFactory().createEntityManager();
try {
model.DemoCustomer cust = em.find(model.DemoCustomer.class, (long)2);
System.out.println(cust.getCustFirstName());
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
} finally {
em.close();
System.out.println("cerrado!");
}
}
}
37) Edit the Generated Class and add schema=”TESTUSER” to the table annotation like you see on line 13.
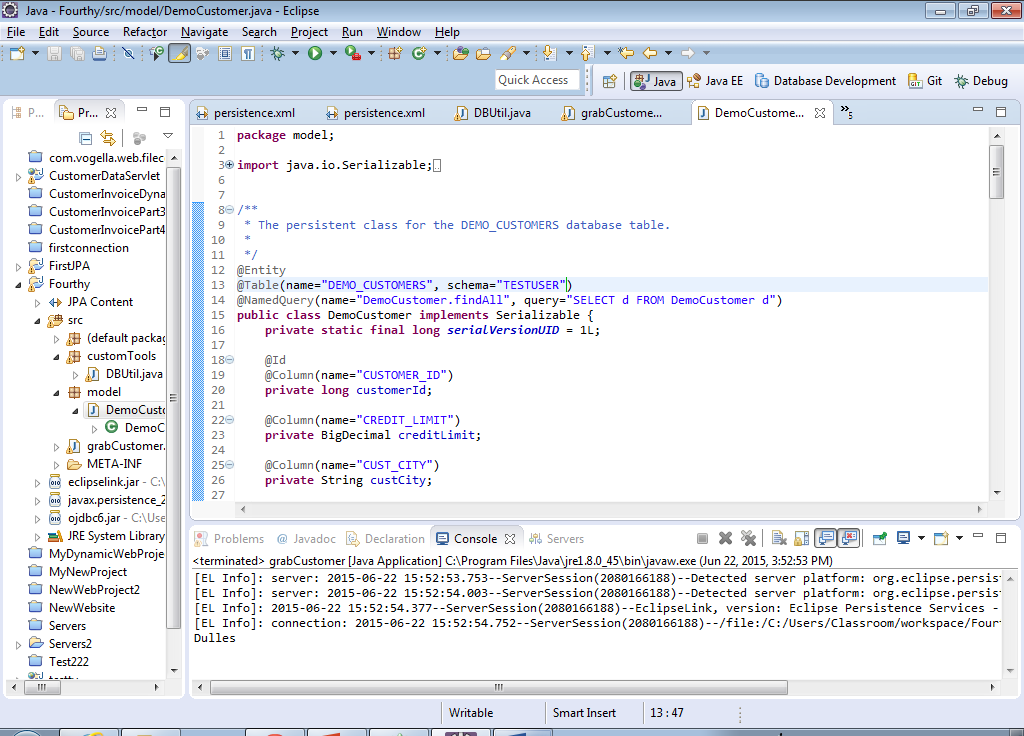
38) Now you are done…Run it and you should see the Customer name (and no errors).
If it didn’t work then most likely you’ve skipped a step or have a typo. Go through the tutorial again - this time reviewing your work.